
Electricity
It's a form or energy produced by the flow of charge through materials and devices under the influence of an electromotive force electrostatically, chemically, mechanically or thermally.

Current
It's a electrons flow through a conductor. Direct current (DC): current in a circuit in one direction only. Alternanting current (AC): an electrical current that periodically changes in magnitue and in direction.
Voltage
It's the unit of force that caused current when included in a closed circuit. one volt causes a current of one ampere through a resistance of one ohm. It's unit is the volt (V).
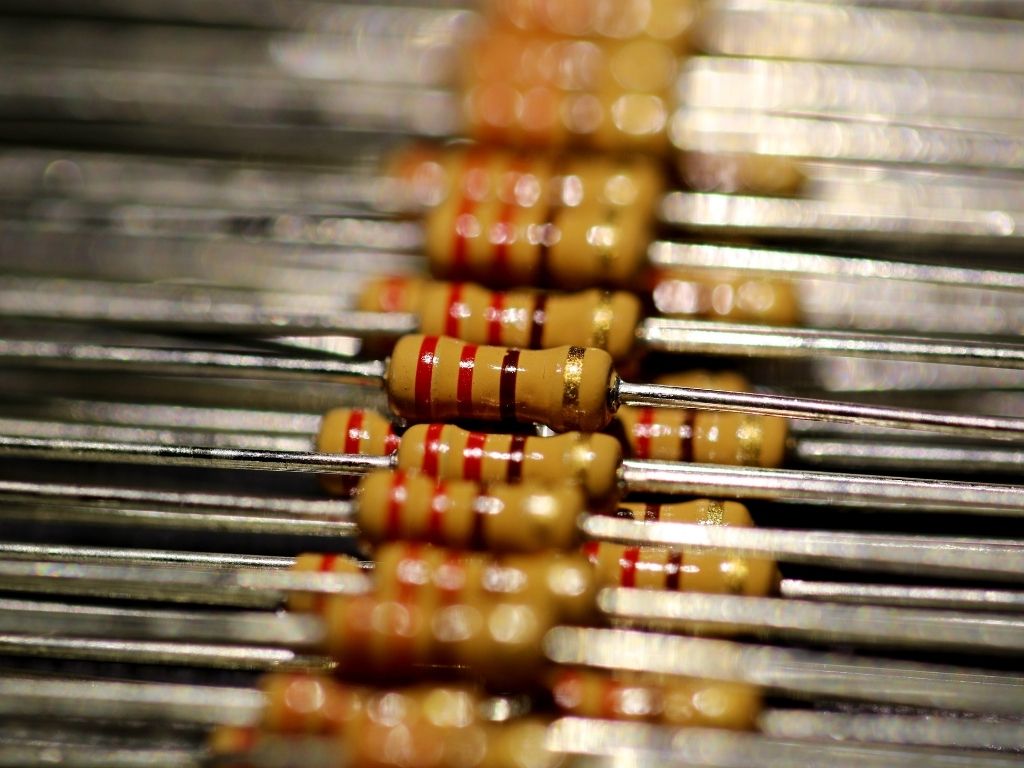

Resistor
It's a passive electrical component that creates resistance in the flow of electric current. The resistance is measured in ohms (Ω).



